Main Points In Hindi (मुख्य बातें – हिंदी में)
यहां प्रकाश संश्लेषण और पेटीएम डोमेन के शोध के मुख्य बिंदु दिए गए हैं:
-
प्रकाश संश्लेषण की प्रक्रिया: पौधे प्रकाश को रासायनिक ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करने के लिए विभिन्न प्रोटीनों की जटिल अंतःक्रियाओं पर निर्भर करते हैं, जिसमें साइटोक्रोम b6f कॉम्प्लेक्स एक केंद्रीय भूमिका निभाता है।
-
पेटीएम डोमेन का अध्ययन: टमाटर के पौधों में पेटीएम डोमेन की भूमिका का अध्ययन CRISPR/Cas9 नॉकआउट तकनीक द्वारा किया गया, जिससे उच्च और कम प्रकाश स्थितियों में इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन और वर्णक उत्पादन में महत्वपूर्ण परिवर्तन सामने आए।
-
उच्च प्रकाश में प्रभाव: पेटीएम प्रोटीन की कमी के कारण पौधों में इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन में कमी आई, जिससे कम कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड संयोजन और क्लोरोफिल, कैरोटीनॉयड स्तर में बदलाव हुआ। यह उच्च प्रकाश के दौरान फोटो अवरोध का कारण बना।
-
कृषि पर प्रभाव: यह शोध कृषि सेटिंग्स में प्रकाश संश्लेषण दक्षता बढ़ाने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हो सकता है, विशेष रूप से खाद्य सुरक्षा और जलवायु परिवर्तन के संदर्भ में। पेटीएम डोमेन के अध्ययन से फसल पैदावार बढ़ाने के लिए आनुवंशिक इंजीनियरिंग की दिशा में नए अवसर मिल सकते हैं।
- वैश्विक खाद्य सुरक्षा चुनौतियाँ: यह अध्ययन स्थायी कृषि के लिए रणनीतियों के विकास में सहायक हो सकता है और तीव्र धूप वाले क्षेत्रों में फसलों के लचीलेपन में सुधार कर सकता है।
Main Points In English(मुख्य बातें – अंग्रेज़ी में)
Here are the main points regarding the role of the PetM domain in photosynthesis as discussed in the provided text:


-
Central Role of Cytochrome b6f Complex: The process of photosynthesis in plants, which converts light into chemical energy, relies on the intricate interaction of various proteins, with the cytochrome b6f complex serving as a key player facilitating the electron flow between Photosystem II and Photosystem I.
-
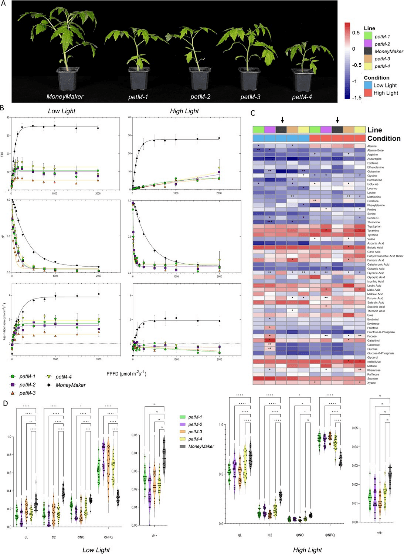
Research on Tomato Plants: Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, in collaboration with international partners, used CRISPR/Cas9 technology to knockout the PetM domain gene in tomato plants. This led to significant changes in electron transport and pigment production under varying light intensities, underlining the importance of this protein in optimizing photosynthetic processes.
-
Effects of PetM Knockout: The removal of the PetM gene resulted in lower electron transport and altered levels of chlorophyll and carotenoids under both low and high light conditions. The study found that PetM helps stabilize the cytochrome b6f complex, ensuring efficient electron transport and preventing harmful reactive oxygen species, highlighting its evolutionary significance for adaptation to terrestrial environments.
-
Implications for Agriculture: Understanding how the PetM domain stabilizes the cytochrome b6f complex under different lighting conditions could enhance photosynthetic efficiency in agricultural settings, particularly for crops like tomatoes, addressing global food security challenges and improving resilience in various environmental conditions.
- Potential for Genetic Engineering: The research suggests that increasing electron transport efficiency, especially in high-light conditions, represents a promising target for genetic engineering aimed at boosting crop yields and improving photosynthetic stability across diverse environmental scenarios.
Complete News In Hindi(पूरी खबर – हिंदी में)
प्रकाश संश्लेषण, वह प्रक्रिया जिसके द्वारा पौधे प्रकाश को रासायनिक ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करते हैं, विभिन्न प्रोटीनों की जटिल अंतःक्रिया पर निर्भर करती है। इस प्रणाली में एक केंद्रीय खिलाड़ी साइटोक्रोम है b6f कॉम्प्लेक्स, जो फोटोसिस्टम II और फोटोसिस्टम I के बीच इलेक्ट्रॉन प्रवाह को सुविधाजनक बनाता है। हालांकि, टमाटर जैसी फसल प्रजातियों में इस तंत्र का अध्ययन करना मुश्किल साबित हुआ है। इन चुनौतियों के कारण, उतार-चढ़ाव वाली प्रकाश स्थितियों के तहत स्थिर प्रकाश संश्लेषक प्रक्रियाओं को बनाए रखने में पेटीएम डोमेन की भूमिका का पता लगाने के लिए आगे का शोध आवश्यक था।
8 नवंबर, 2023 को मैक्स-प्लैंक-इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ मॉलिक्यूलर प्लांट फिजियोलॉजी के वैज्ञानिकों ने अंतरराष्ट्रीय सहयोगियों के साथ, प्रकाशित (DOI: 10.1093/घंटा/uhad224) में उनका शोध बागवानी अनुसंधान. अध्ययन में CRISPR/Cas9 नॉकआउट तकनीक का उपयोग करके टमाटर में PetM डोमेन युक्त प्रोटीन को एन्कोड करने वाले जीन के कार्य की जांच की गई। पेटीएम जीन नॉकआउट के कारण अलग-अलग प्रकाश तीव्रता के तहत इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन और वर्णक उत्पादन में महत्वपूर्ण बदलाव आया, जिससे प्रकाश संश्लेषक अनुकूलन में प्रोटीन की भूमिका रेखांकित हुई। इन निष्कर्षों से उच्च फसल पैदावार के लिए प्रकाश संश्लेषण को अनुकूलित करने में सफलता मिल सकती है।
शोध ने इसे हटाने के शारीरिक और चयापचय प्रभाव का पता लगाया पेटीएम टमाटर के पौधों में जीन. कम और उच्च प्रकाश दोनों के तहत, नॉकआउट लाइनों ने कम इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन और सीओ प्रदर्शित किया2 क्लोरोफिल और कैरोटीनॉयड स्तर में परिवर्तन के साथ-साथ आत्मसात। जबकि पौधों ने बेसल CO बनाए रखा2 कम रोशनी में स्तर, उच्च रोशनी की स्थिति के कारण फोटो अवरोध उत्पन्न हुआ। इसके अतिरिक्त, मेटाबोलिक प्रोफाइल से ग्लाइसेरिक एसिड में कमी और प्रमुख अमीनो एसिड में परिवर्तन का पता चला। इन परिणामों से पता चलता है कि पेटीएम प्रोटीन उच्च प्रकाश के तहत साइटोक्रोम बी6एफ कॉम्प्लेक्स को स्थिर करने में मदद करता है, कुशल इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन सुनिश्चित करता है और हानिकारक प्रतिक्रियाशील ऑक्सीजन प्रजातियों को रोकता है, जो स्थलीय वातावरण के अनुकूल होने में इसके विकासवादी महत्व को उजागर करता है।
मैक्स-प्लैंक-इंस्टीट्यूट के डॉ. एलिसडेयर आर. फर्नी ने निष्कर्षों के व्यापक प्रभाव पर जोर दिया: “हालांकि पेटीएम डोमेन का अध्ययन मॉडल जीवों में किया गया है, हमारा शोध इस ज्ञान को टमाटर, एक प्रमुख फसल प्रजाति तक विस्तारित करता है। यह समझना कि पेटीएम डोमेन विभिन्न प्रकाश स्थितियों के तहत साइटोक्रोम b6f कॉम्प्लेक्स को कैसे स्थिर करता है, कृषि सेटिंग्स में प्रकाश संश्लेषण दक्षता को बढ़ाने का द्वार खोलता है। यह विशेष रूप से महत्वपूर्ण है क्योंकि हम खाद्य सुरक्षा और जलवायु लचीलेपन में वैश्विक चुनौतियों का सामना कर रहे हैं।”
प्रकाश संश्लेषण में पेटीएम डोमेन की भूमिका की पहचान के महत्वपूर्ण कृषि निहितार्थ हो सकते हैं। इलेक्ट्रॉन परिवहन दक्षता को बढ़ाना, विशेष रूप से उच्च-प्रकाश स्थितियों में, फसल की पैदावार बढ़ाने के उद्देश्य से आनुवंशिक इंजीनियरिंग के लिए एक आशाजनक लक्ष्य प्रदान करता है। प्रकाश संश्लेषण को स्थिर करने से विभिन्न पर्यावरणीय परिस्थितियों में फसल के लचीलेपन में सुधार हो सकता है, खासकर तीव्र धूप वाले क्षेत्रों में। यह शोध वैश्विक खाद्य सुरक्षा चुनौतियों का समाधान करते हुए फसल विकास और टिकाऊ कृषि में नवीन रणनीतियों में योगदान दे सकता है।
###
संदर्भ
डीओआई
मूल स्रोत यूआरएल
https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhad224
फंडिंग संबंधी जानकारी
एएन-एन को कॉन्सेल्हो नैशनल डी डेसेनवोलविमेंटो सिएंटिफिको ई टेक्नोलोजिको (सीएनपीक्यू-ब्राजील) द्वारा प्रदान की गई शोध फेलोशिप। कृतज्ञतापूर्वक स्वीकार किया जाता है। एआरएफ और एसए यूरोपीय संघ के होराइजन 2020 अनुसंधान और नवाचार कार्यक्रम, प्रोजेक्ट प्लांटासिस्ट (एफपीए नंबर 664620 के तहत एसजीए-सीएसए नंबर 739582), और बीजी05एम2ओपी001-1.003-001-सी01 परियोजना को स्वीकार करते हैं, जो यूरोपीय क्षेत्रीय विकास कोष द्वारा वित्तपोषित है। बल्गेरियाई ‘स्मार्ट ग्रोथ के लिए विज्ञान और शिक्षा’ परिचालन कार्यक्रम। SA EU Horizon 2020 को स्वीकार करता है, HORIZON-WIDERA-2022-TALENTS-01, प्रोजेक्ट NetGenCrop (अनुदान समझौता संख्या 101087091) को कॉल करें।
के बारे में बागवानी अनुसंधान
बागवानी अनुसंधान नानजिंग कृषि विश्वविद्यालय की एक ओपन एक्सेस पत्रिका है और क्लैरिवेट, 2022 से जर्नल उद्धरण रिपोर्ट ™ की बागवानी श्रेणी में नंबर एक स्थान पर है। पत्रिका मूल शोध लेख, समीक्षा, दृष्टिकोण, टिप्पणियां, पत्राचार लेख और पत्र प्रकाशित करने के लिए प्रतिबद्ध है। जैव प्रौद्योगिकी, प्रजनन, सेलुलर और आणविक जीव विज्ञान, विकास, आनुवंशिकी, अंतर-प्रजाति परस्पर क्रिया, शरीर विज्ञान और फसलों की उत्पत्ति और पालतूकरण सहित सभी प्रमुख बागवानी पौधों और विषयों से संबंधित संपादक।
Complete News In English(पूरी खबर – अंग्रेज़ी में)
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light into chemical energy, and it relies on complex interactions among various proteins. A key component in this system is the cytochrome b6f complex, which helps facilitate the flow of electrons between Photosystem II and Photosystem I. However, studying this mechanism in crop species like tomatoes has proven to be challenging. Due to these challenges, further research is required to explore the role of the PetM domain in maintaining stable photosynthetic processes under fluctuating light conditions.
On November 8, 2023, researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, along with international collaborators, published their findings in Horticultural Research (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhad224). The study investigated the function of the gene encoding a PetM domain protein in tomatoes using CRISPR/Cas9 knockout technology. The knockout of the PetM gene resulted in significant changes in electron transport and pigment production under varying light intensities, highlighting the protein’s role in photosynthetic optimization. These findings could lead to advancements in optimizing photosynthesis for higher crop yields.
The research also explored the physiological and metabolic effects of removing the PetM gene in tomato plants. Under both low and high light conditions, the knockout lines showed reduced electron transport and changes in CO2 absorption, chlorophyll, and carotenoid levels. While the plants maintained basal CO2 levels under low light, high light conditions caused photo-inhibition. Additionally, the metabolic profile indicated a decrease in glyceric acid and changes in key amino acids. These results suggest that the PetM protein helps stabilize the cytochrome b6f complex under high light, ensuring efficient electron transport and preventing harmful reactive oxygen species, which underscores its evolutionary significance for adaptation to terrestrial environments.
Dr. Alisdair R. Fernie from the Max Planck Institute emphasized the broader implications of the findings: “Although the PetM domain has been studied in model organisms, our research extends this knowledge to tomatoes, a major crop species. Understanding how the PetM domain stabilizes the cytochrome b6f complex under various light conditions opens the door to enhancing photosynthetic efficiency in agricultural settings. This is particularly important as we face global challenges related to food security and climate resilience.”
Identifying the role of the PetM domain in photosynthesis could have significant agricultural implications. Enhancing electron transport efficiency, especially under high-light conditions, provides a promising target for genetic engineering aimed at increasing crop yields. Stabilizing photosynthesis may improve crop resilience to various environmental conditions, particularly in regions with intense sunlight. This research could contribute to innovative strategies for crop development and sustainable agriculture, addressing global food security challenges.
###
References
DOI
Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhad224
Funding Information
Research fellowship provided by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil). Funding accepted by ARF and SA under the European Union Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program, Plantassist Project (FP4 No. 664620 under SGA-CSA No. 739582), and BG05M2OP001-1.003-001-C01 project funded by the European Regional Development Fund. SA accepts EU Horizon 2020 through the HORIZON-WIDERA-2022-TALENTS-01 call, Project NetGenCrop (Grant Agreement No. 101087091).
About Horticultural Research
Horticultural Research is an open-access journal from Nanjing Agricultural University and has been ranked first in the horticulture category of the Clarivate Journal Citation Reports™ since 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence, and letters related to all major horticultural plants and topics, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, development, genetics, interspecies interactions, physiology, and crop origin and domestication.