Main Points In Hindi (मुख्य बातें – हिंदी में)
यहां मैकाडामिया प्रजातियों के जीनोम अनुक्रमण से संबंधित अध्ययन के मुख्य बिंदु दिए गए हैं:
-
जीनोम अनुक्रमण का महत्व: चार मैकाडामिया प्रजातियों का सफल जीनोम अनुक्रमण फसल सुधार के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रगति दर्शाता है, जिसमें रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता, जलवायु अनुकूलनशीलता और फसल की उपज को बढ़ाने के लिए आनुवंशिक लक्षणों का पता लगाया गया है।
-
चुनौतियाँ और समाधान: अध्ययन में यह भी बताया गया है कि सीमित आनुवंशिक विविधता, मुख्य रूप से हवाईयन जर्मप्लाज्म से, मैकाडामिया के प्रजनन में चुनौतियाँ उत्पन्न कर रही हैं। नए जीनोमिक डेटा का उपयोग करके इस विविधता को बढ़ाने की संभावनाएं हैं।
-
नवीनतम तकनीक का उपयोग: शोधकर्ताओं ने PacBio HiFi अनुक्रमण तकनीक का उपयोग करके जीनोम असेंबली की, जिससे उत्कृष्ट जीनोम पूर्णता प्राप्त हुई और विभिन्न प्रजातियों के बीच संरचनात्मक भिन्नताओं की पहचान की गई।
-
अध्ययन के लाभ: सभी चार प्रजातियों का जीनोम अनुक्रमण आहार में वांछनीय गुणों को बनाए रखते हुए धारणात्मक विविधता को बढ़ाने में मदद कर सकता है, जो वैश्विक उत्पादन और फसल लचीलेपन को सुधारने की क्षमता प्रदान करता है।
- भविष्य की दृष्टि: इस अध्ययन से प्राप्त डेटा प्रजनकों और शोधकर्ताओं के लिए एक मूल्यवान उपकरण है, जो बदलती जलवायु और बढ़ती वैश्विक मांगों के संदर्भ में आर्थिक दृष्टि से महत्वपूर्ण मैकाडामिया फसल की भविष्यवाणी में मदद करेगा।
Main Points In English(मुख्य बातें – अंग्रेज़ी में)
Here are the main points of the article:


-
Successful Genome Sequencing: A research team has successfully sequenced and assembled the genomes of four macadamia species, marking a significant advancement for crop improvement efforts of this commercially valuable nut.
-
Genetic Insights: The findings reveal important genetic traits that can enhance disease resistance, climate adaptability, and yield potential, addressing the challenges of genetic diversity in macadamia breeding programs.
-
Narrow Genetic Base: Despite the growing global importance of macadamia nuts, the species have a narrow genetic base primarily derived from Hawaiian germplasm, limiting their genetic diversity and resilience.
-
High-Quality Genome Assembly: The study utilized PacBio HiFi long-read sequencing technology to achieve high-quality genome assemblies with over 97% completeness, helping to reveal structural variations and genetic diversity among the species.
- Future Breeding Programs: The comprehensive genomic sequencing of all four macadamia species provides valuable resources for breeders, aiming to improve crop resilience and productivity to meet the demands of a changing climate and global markets.
Complete News In Hindi(पूरी खबर – हिंदी में)
एक शोध दल ने इन चारों के जीनोम को सफलतापूर्वक अनुक्रमित और एकत्रित किया है मैकाडामिया प्रजाति, इस व्यावसायिक रूप से मूल्यवान अखरोट के लिए फसल सुधार प्रयासों में एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रगति का प्रतीक है। निष्कर्षों से प्रमुख आनुवंशिक लक्षणों का पता चलता है जो मैकाडामिया प्रजनन में आनुवंशिक विविधता की चुनौतियों का समाधान करते हुए रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता, जलवायु अनुकूलनशीलता और फसल की उपज को बढ़ा सकते हैं।
मैकाडामियापूर्वी ऑस्ट्रेलिया के मूल निवासी एक जीनस में चार प्रजातियां शामिल हैं: मैकाडामिया इंटीग्रिफोलिया, एम. टेट्राफिला, एम. टर्निफ़ोलियाऔर एम. जानसेनी. व्यावसायिक उत्पादन के लिए केवल पहली दो प्रजातियों और उनके संकरों की व्यापक रूप से खेती की जाती है। वैश्विक फसल के रूप में इसके बढ़ते महत्व के बावजूद, मैकाडामिया को एक संकीर्ण आनुवंशिक आधार, मुख्य रूप से हवाईयन जर्मप्लाज्म से पालतू बनाया गया है, जिसने इसकी आनुवंशिक विविधता और लचीलेपन को सीमित कर दिया है। इस अध्ययन का उद्देश्य सभी चार प्रजातियों की उच्च गुणवत्ता वाली जीनोम असेंबली के माध्यम से मैकाडामिया के लिए उपलब्ध आनुवंशिक संसाधनों का विस्तार करना है।
ए अध्ययन (डीओआई: 10.48130/टीपी-0024-0029) में प्रकाशित उष्णकटिबंधीय पौधे 21 अक्टूबर 2024 को, मैकाडामिया नट्स के स्वाद और तेल सामग्री जैसे वांछनीय गुणों को बनाए रखने या बढ़ाने के दौरान जीन पूल को चौड़ा करने, लचीलापन बढ़ाने में मदद करता है।
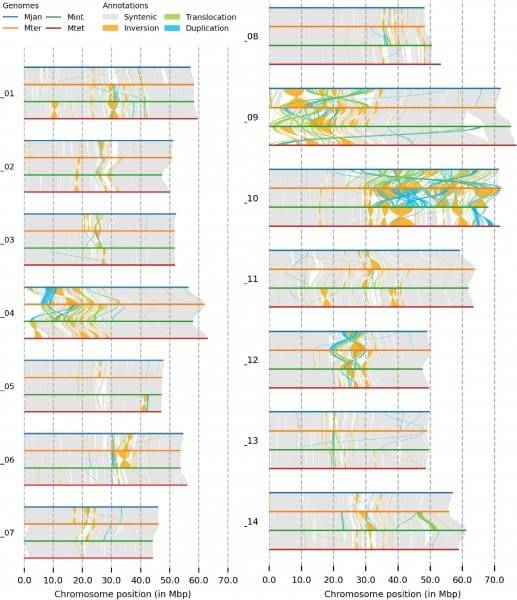
शोधकर्ताओं ने चार के जीनोम को इकट्ठा करने के लिए PacBio HiFi लंबे समय से पढ़ी जाने वाली अनुक्रमण तकनीक का उपयोग किया मैकाडामिया प्रजातियाँ: एम. जानसेनीमैं, एम. इंटीग्रिफोलिया, एम. टेट्राफिलाऔर एम. टर्निफ़ोलिया, 27X और 42X के बीच अनुक्रमण गहराई प्राप्त करना। असेंबलियों ने 45 एमबी से अधिक एन50 मूल्यों के साथ अत्यधिक सन्निहित जीनोम का उत्पादन किया, जो उत्कृष्ट जीनोम पूर्णता का संकेत देता है। प्रजातियों में से, एम. इंटीग्रिफ़ोलिया में सबसे अधिक संख्या में कंटिग्स थे एम. टेट्राफिला सबसे कम था. BUSCO विश्लेषण ने 97% से अधिक की जीनोम पूर्णता की पुष्टि की, जिसमें अधिकांश जीन एकल-प्रतिलिपि के रूप में पहचाने गए। अध्ययन में क्रोमोसोम-स्तर की असेंबली भी आयोजित की गई, जिसमें जीनोम का आकार 735 एमबी से 795 एमबी तक था। एम. टेट्राफिला जबकि, सबसे बड़ी ध्वस्त विधानसभा थी एम. जानसेनी सबसे छोटा था. शोधकर्ताओं ने सभी प्रजातियों में गुणसूत्र 9 और 10 में संरचनात्मक भिन्नताओं की पहचान की। जीनोम एनोटेशन से पता चला कि 61% से 62% जीनोम में दोहराव वाले तत्व शामिल थे, और अनुमानित जीन की संख्या 37,198 से 40,534 तक थी। विशेष रूप से, फैटी एसिड जैवसंश्लेषण और रोगाणुरोधी गुणों से जुड़े जीन को सभी प्रजातियों में संरक्षित किया गया था। तुलनात्मक विश्लेषण ने प्रजातियों के बीच महत्वपूर्ण संरचनात्मक अंतर की पहचान की, जिससे प्रजातियों के भीतर आनुवंशिक विविधता की समझ में वृद्धि हुई मैकाडामिया जीनस. ये अंतर्दृष्टि रोग प्रतिरोध और जलवायु अनुकूलन क्षमता जैसी चुनौतियों का समाधान करने के लिए जंगली प्रजातियों की आनुवंशिक विविधता का लाभ उठाकर मैकाडामिया प्रजनन कार्यक्रमों में सुधार के लिए आधार तैयार करती है।
अध्ययन के प्रमुख शोधकर्ता, डॉ. रॉबर्ट जे. हेनरी के अनुसार, “सभी चार मैकाडामिया प्रजातियों के जीनोम तक पहुंच होने से फसल के लचीलेपन और उत्पादकता में सुधार के अभूतपूर्व अवसर मिलते हैं। यह व्यापक जीनोमिक डेटा अधिक सूचित प्रजनन कार्यक्रमों के लिए आधार प्रदान करता है, जो हैं बदलती जलवायु और बढ़ते वैश्विक बाज़ारों की माँगों को पूरा करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।”
सभी चार मैकाडामिया प्रजातियों का यह व्यापक अनुक्रमण, वैश्विक उत्पादन को बढ़ावा देने और फसल लचीलेपन में सुधार करने की क्षमता के साथ, मैकाडामिया प्रजनन में महत्वपूर्ण प्रगति के लिए आधार तैयार करता है। नया जीनोमिक डेटा बदलती दुनिया में इस आर्थिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण फसल के भविष्य को सुरक्षित करने के लिए काम करने वाले प्रजनकों और शोधकर्ताओं के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण उपकरण प्रदान करता है।
###
संदर्भ
डीओआई
मूल स्रोत यूआरएल
https://www.maxapress.com/article/doi/10.48130/tp-0024-0029
फंडिंग संबंधी जानकारी
इस परियोजना को क्वींसलैंड विश्वविद्यालय के सह-निवेश और ऑस्ट्रेलियाई सरकार के योगदान के साथ, हॉर्ट इनोवेशन द्वारा विकसित हॉर्ट फ्रंटियर्स रणनीतिक साझेदारी पहल के हिस्से के रूप में हॉर्ट फ्रंटियर्स एडवांस्ड प्रोडक्शन सिस्टम फंड द्वारा वित्त पोषित किया गया था। आरएच को ऑस्ट्रेलियाई अनुसंधान परिषद (सीई200100015) द्वारा वित्त पोषित किया गया था।
के बारे में उष्णकटिबंधीय पौधे
उष्णकटिबंधीय पौधे (ई-आईएसएसएन 2833-9851) हैनान विश्वविद्यालय की आधिकारिक पत्रिका है और मैक्सिमम एकेडमिक प्रेस द्वारा प्रकाशित है। उष्णकटिबंधीय पौधे कठोर सहकर्मी समीक्षा से गुजरता है और अनुसंधान निष्कर्षों के तेजी से प्रसार को सक्षम करने, अकादमिक ज्ञान के आदान-प्रदान की सुविधा प्रदान करने और उष्णकटिबंधीय पौधों के अनुसंधान में उभरती नवीन प्रौद्योगिकियों और मुद्दों पर अकादमिक चर्चा को प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए ओपन-एक्सेस प्रारूप में प्रकाशित किया जाता है।
Complete News In English(पूरी खबर – अंग्रेज़ी में)
A research team has successfully sequenced and compiled the genomes of four macadamia species, marking a significant advancement for efforts to improve this commercially valuable nut. The findings uncover key genetic traits that could help address challenges with genetic diversity in macadamia breeding while enhancing disease resistance, adaptability to climate, and crop yield.
The macadamia genus, native to eastern Australia, includes four species: Macadamia integrifolia, M. tetraphylla, M. ternifolia, and M. jansenii. Of these, only the first two species and their hybrids are widely cultivated for commercial production. Despite its growing significance as a global crop, macadamia has been developed mainly from a narrow genetic base, primarily from Hawaiian germplasm, which has limited its genetic diversity and resilience. This study aims to expand the genetic resources available for macadamia through high-quality genome assemblies of all four species.
A study published in Tropical Plants on October 21, 2024, discusses how broadening the gene pool can help maintain or enhance desirable traits like taste and oil content in macadamia nuts while increasing resilience.
The researchers used PacBio HiFi long-read sequencing technology to gather genomes of the four macadamia species: M. jansenii, M. integrifolia, M. tetraphylla, and M. ternifolia, achieving sequencing depths between 27X and 42X. The assemblies produced highly contig-structured genomes with N50 values exceeding 45 MB, indicating excellent genome completeness. Among the species, M. integrifolia had the highest number of contigs, while M. tetraphylla had the least. BUSCO analysis confirmed that the genome completeness exceeded 97%, with most genes identified as single-copy. The study also included chromosome-level assemblies with genome sizes ranging from 735 MB to 795 MB, where M. tetraphylla had the largest and M. jansenii the smallest genome. Researchers identified structural variations in chromosomes 9 and 10 across all species. Genome annotation revealed that 61% to 62% of the genome contained repetitive elements, with an estimated gene count ranging from 37,198 to 40,534. Notably, genes related to fatty acid biosynthesis and antimicrobial properties were preserved across all species. Comparative analysis identified significant structural differences among the species, enhancing the understanding of genetic diversity within the macadamia genus. These insights lay the groundwork for improving macadamia breeding programs by leveraging the genetic diversity of wild species to address challenges such as disease resistance and climate adaptability.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. Robert J. Henry, “Access to the genomes of all four macadamia species presents unprecedented opportunities to enhance crop resilience and productivity. This comprehensive genomic data provides a foundation for more informed breeding programs, which are critical to meeting the demands of changing climates and growing global markets.”
This extensive sequencing of all four macadamia species lays the foundation for significant progress in macadamia breeding, with the potential to boost global production and improve crop resilience. The new genomic data serves as a vital tool for breeders and researchers working to secure the future of this economically important crop in a changing world.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
https://www.maxapress.com/article/doi/10.48130/tp-0024-0029
Funding Information
This project was funded by Horticulture Innovation as part of the Horticulture Frontiers Strategic Partnership Initiative, co-invested by the University of Queensland and with contributions from the Australian government. RH was supported by the Australian Research Council (CE200100015).
About Tropical Plants
Tropical Plants (e-ISSN 2833-9851) is the official journal of Hainan University, published by Maximum Academic Press. Tropical Plants undergoes rigorous peer review and is published in an open-access format to facilitate the rapid dissemination of research findings, promote the exchange of academic knowledge, and encourage academic discussions on emerging technologies and issues in tropical plant research.