Main Points In Hindi (मुख्य बातें – हिंदी में)
यहां जलवायु परिवर्तन के कृषि पर प्रभाव के मुख्य बिंदु दिए गए हैं:
-
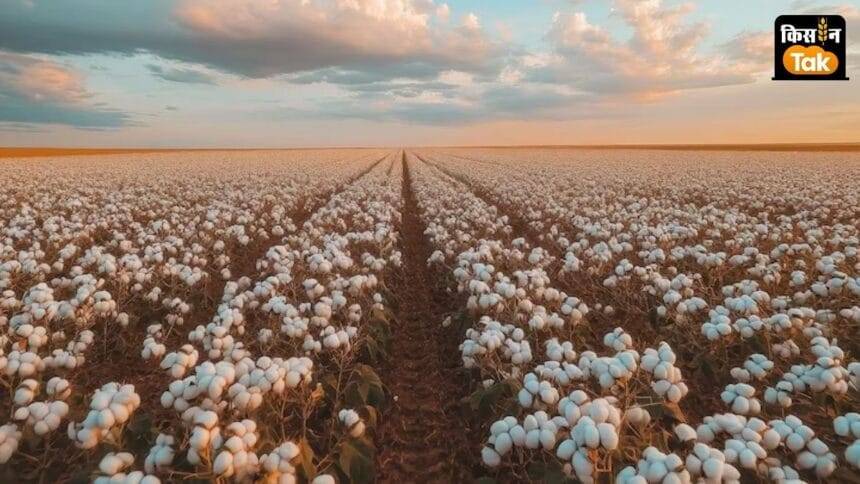
जलवायु परिवर्तन का प्रतिकूल प्रभाव: गुजरात और महाराष्ट्र में कपास की खेती पर जलवायु परिवर्तन के गंभीर असर हुए हैं। रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, पिछले 5 वर्षों में 50 प्रतिशत से अधिक किसान जलवायु परिवर्तनों के नकारात्मक प्रभावों का सामना कर रहे हैं, जैसे बाढ़, बारिश, गर्मी और उच्च तापमान के कारण फसलों को नुकसान।
-
सर्वेक्षण के निष्कर्ष: अंतरराष्ट्रीय संस्थान और भारतीय आपदा न्यूनीकरण संस्थान द्वारा किए गए सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार, लगभग दो तिहाई किसानों ने लंबे सूखे, उच्च तापमान, और अत्यधिक गर्म दिन का सामना किया है। सर्वेक्षण में शामिल अधिकतर किसान छोटे भूमि मालिक थे (10 एकड़ से कम)।
-
कपास का क्षेत्रफल घटा: भारत दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा कपास उत्पादक है। हालांकि, जलवायु परिवर्तनों के कारण पिछले खरिफ मौसम में कपास की खेती में बुरी तरह से नुकसान हुआ, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप इस वर्ष लगभग 11 लाख हेक्टेयर में कपास का क्षेत्रफल घट गया है।
-
किसानों की अनुकूलन रणनीतियाँ: किसान जलवायु खतरों का सामना करने के लिए अपनी फसलों में विविधता लाने, खेती के तरीकों में बदलाव करने, और सिंचाई संसाधनों में निवेश करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित कर रहे हैं। कुछ किसान पीएम फसल बीमा का लाभ उठाकर अपने नुकसान की भरपाई करने की कोशिश कर रहे हैं।
- आर्थिक चुनौतियाँ: कई किसान लोन लेने की कोशिश कर रहे हैं या अपने मवेशियों को बेचकर अपने नुकसान को कवर करने का प्रयास कर रहे हैं, जो उनकी आर्थिक स्थिरता पर प्रतिकूल प्रभाव डाल रहा है।
Main Points In English(मुख्य बातें – अंग्रेज़ी में)
-
Adverse Impact on Cotton Farmers: Over 50% of cotton farmers in Gujarat and Maharashtra have experienced significant challenges due to climate change, including losses attributed to floods, excessive rains, and high temperatures.
-
Extended Drought and Extreme Weather: A survey revealed that two-thirds of 360 farmers reported facing longer periods of drought, elevated temperatures, and an increase in extreme heat days over the past five years in the affected regions.
-
Reduction in Cotton Cultivation Area: Due to the adverse effects of climate change, cotton cultivation in India has declined by approximately 11 lakh hectares from the previous year, with only 112.76 lakh hectares planted in the current Kharif season.
-
Adaptation Strategies by Farmers: To counter climate challenges, farmers are diversifying their crop choices, modifying farming practices, investing in irrigation, and some are utilizing government crop insurance programs. However, many also resort to loans or selling livestock to mitigate losses.
- Demographics of Affected Farmers: The survey mostly included farmers owning less than 10 acres of land, highlighting the vulnerability of smallholder farmers in the face of climate-induced agricultural challenges.


Complete News In Hindi(पूरी खबर – हिंदी में)
जलवायु परिवर्तन का प्रभाव कृषि पर越来越明显 है। हाल की रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, पिछले 5 वर्षों में गुजरात और महाराष्ट्र में कपास की खेती पर सबसे अधिक प्रतिकूल प्रभाव पड़ा है। 50 प्रतिशत से अधिक किसानों को जलवायु परिवर्तन के नकारात्मक प्रभावों का सामना करना पड़ा है। बाढ़, बारिश, गर्मी और उच्च तापमान के कारण फसलों को नुकसान हुआ है। आगे आने वाले समय में यह नुकसान और बढ़ने की संभावना है।
यूके के थिंक टैंक इंटरनेशनल इंस्टीट्यूट फॉर एनवायरनमेंट एंड डेवलपमेंट (IIED) और ऑल इंडिया डिजास्टर मिटिगेशन इंस्टीट्यूट (AIDMI) द्वारा किए गए सर्वेक्षण में, 360 किसानों में से लगभग दो-तिहाई किसानों का सामना लंबे सूखे, उच्च तापमान और अधिक दिनों की चरम गर्मी से हुआ है। महाराष्ट्र और गुजरात में किए गए 5 वर्षों के इस सर्वे में पाया गया है कि 50 प्रतिशत से अधिक कपास किसान जलवायु परिवर्तन के प्रतिकूल प्रभावों का सामना कर रहे हैं।
सर्वेक्षण में 10 एकड़ से कम भूमि वाले किसान शामिल
संस्थान के अनुसार, सितंबर 2023 में किए गए सर्वेक्षण में गुजरात के सुरेन्द्रनगर जिले और महाराष्ट्र के संभाजी नगर जिले के कपास किसानों को शामिल किया गया था। अधिकांश किसान जमीन के मालिक थे, जिनमें से अधिकांश के पास 10 एकड़ से कम जमीन थी। इनमें से 50 प्रतिशत से अधिक किसान जलवायु परिवर्तन के कारण कृषि और उत्पादन समस्याओं का सामना कर रहे हैं।
नुकसान के कारण कपास की खेती में कमी
भारत दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा कपास उत्पादक है। 2023 में, इसने 130 लाख हेक्टेयर में लगभग 58.4 लाख मीट्रिक टन कपास उत्पादन किया। हालाँकि, जलवायु परिवर्तन के कारण पिछले खरीफ मौसम में कपास किसानों को बड़े नुकसान उठाने पड़े। इस कारण कपास की खेती में इस वर्ष लगभग 11 लाख हेक्टेयर की कमी आई है। केंद्रीय कृषि और किसान कल्याण मंत्रालय के अनुसार, इस बार खरीफ मौसम में कपास 112.76 लाख हेक्टेयर में बोई गई है। पिछले वर्ष इसी अवधि में कपास 123.71 लाख हेक्टेयर में बोई गई थी।
किसान जलवायु संकट के समाधान के लिए क्या कर रहे हैं?
सर्वेक्षण रिपोर्ट में कहा गया है कि किसान जलवायु परिवर्तन का सामना करने के लिए अपने फसलों के विविधीकरण पर ध्यान केंद्रित कर रहे हैं। जलवायु संकट का सामना करने के लिए किसानों ने खेती के तरीकों में बदलाव करने या सिँचाई सुविधाओं में निवेश करने की कोशिश की है। हालांकि, कई मामलों में किसानों को ऋण लेना पड़ता है या अपने मवेशियों को बेचकर अपने नुकसान की भरपाई करने की कोशिश करनी पड़ती है। हालांकि, कुछ किसान पीएम फसल बीमा का लाभ भी उठा रहे हैं।
इस पर भी पढ़ें –
Complete News In English(पूरी खबर – अंग्रेज़ी में)
The impact of climate changes is becoming increasingly visible on agriculture. The latest report says that during the last 5 years, the most adverse impact on cotton cultivation has been seen in Gujarat and Maharashtra. More than 50 percent farmers have had to face the adverse effects of climate change. Crops suffered losses due to floods, rains, heat and high temperatures. Whereas, the loss is expected to increase further in the coming time.
Nearly two-thirds of 360 farmers surveyed by UK think tank International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED) and All India Disaster Mitigation Institute (AIDMI) were facing longer drought, higher temperatures and more days of extreme heat. Is facing. It has been said that in the survey conducted over 5 years in Maharashtra and Gujarat, more than 50 percent of the cotton farmers are facing the adverse effects of climate changes.
Farmers owning less than 10 acres of land included in the survey
According to the agency, the survey conducted in September 2023 included cotton farmers evenly distributed between Surendranagar district of Gujarat and Sambhaji Nagar district of Maharashtra. Most of the farmers were land owners, most of whom had less than 10 acres of land. Of these, more than 50 percent farmers are facing problems in farming and production problems due to climate changes.
Cotton area reduced due to loss
India is the largest producer of cotton globally. In 2023, it has achieved cotton production of about 58.4 lakh metric tons in 130 lakh hectares. Whereas, due to climate changes, cotton farmers had to suffer huge losses in the last Kharif season. For this reason, cotton cultivation has decreased in the area of about 11 lakh hectares this year. According to the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, this time in the Kharif season, cotton has been sown in 112.76 lakh hectares across the country. Whereas, in the same period last year, cotton was sown in 123.71 lakh hectare area.
What are farmers doing to deal with climate threats?
The survey report says that farmers are focusing on diversifying their crops to deal with climate changes. Efforts are being made to combat climate threats by changing farming methods or investing in irrigation resources. Whereas, in many cases, farmers have to take loans or are trying to cover their losses by selling their cattle. However, some farmers are also taking advantage of PM crop insurance.